The Ultimate Guide To Companion Planting For Vegetable Gardens
The Ultimate Guide to Companion Planting for Vegetable Gardens
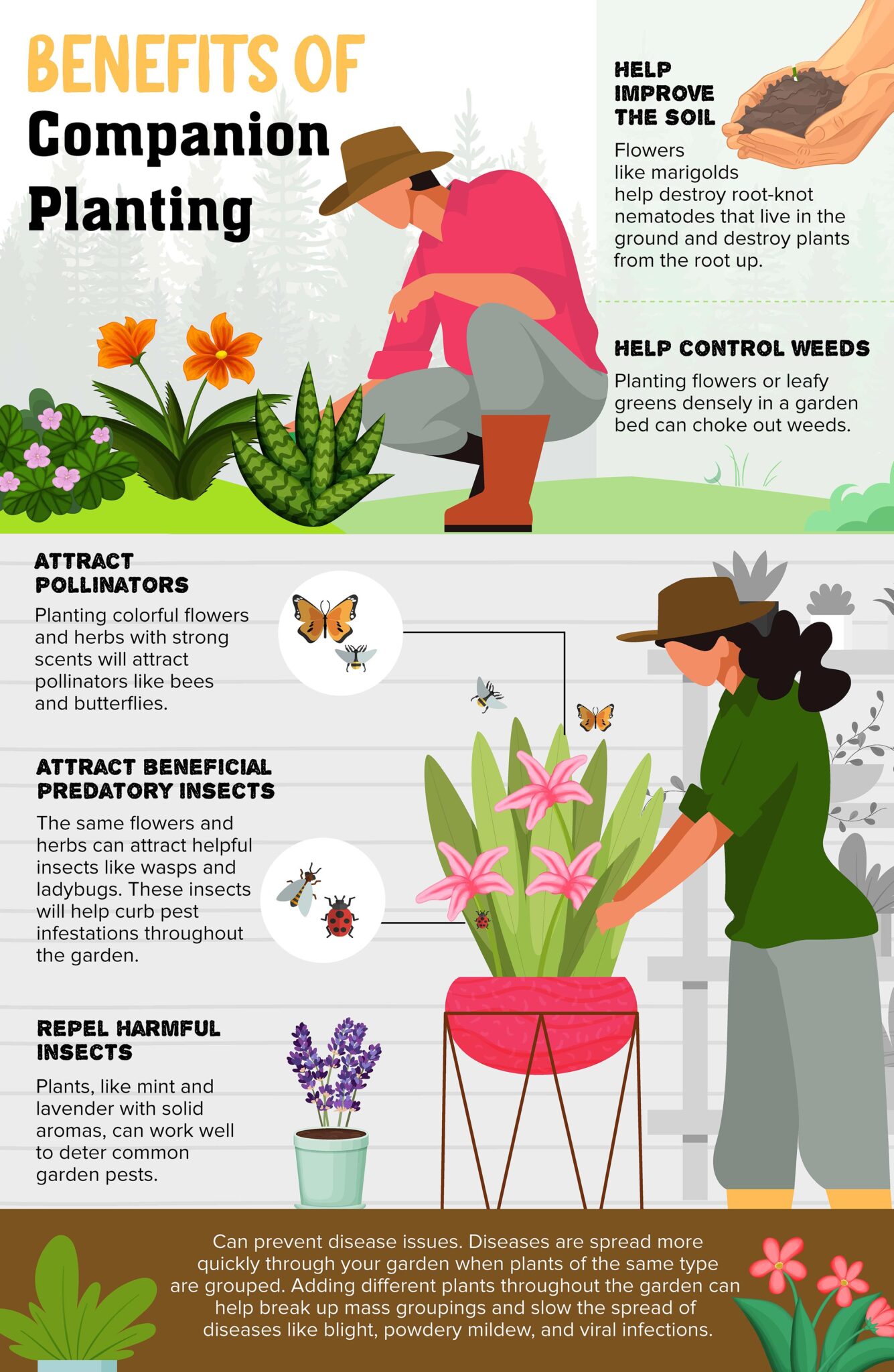
Companion planting is a gardening technique that involves planting certain types of plants together to benefit each other. This can be done to attract beneficial insects, repel pests, improve soil quality, or increase yields.
There are many different companion planting combinations that can be used, but some of the most popular include:
- Tomatoes and basil: Basil repels tomato hornworms and other pests, and it also enhances the flavor of tomatoes.
- Carrots and onions: Onions repel carrot fly larvae, and carrots help to improve the flavor of onions.
- Beans and peas: Beans fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits peas and other legumes.
- Cucumbers and nasturtiums: Nasturtiums attract aphids, which are then eaten by ladybugs and other beneficial insects.
- Lettuce and chives: Chives repel slugs and other pests, and they also add flavor to salads.
These are just a few examples of the many different companion planting combinations that can be used. There are many resources available that can help you to find the best companion plants for your specific garden.
Benefits of Companion Planting
There are many benefits to companion planting, including:
- Reduced pest and disease problems: Companion plants can help to repel pests and attract beneficial insects, which can help to keep your garden healthy.
- Improved soil quality: Some companion plants, such as legumes, can fix nitrogen in the soil, which can improve the overall health of your garden.
- Increased yields: Companion planting can help to increase the yields of some crops. For example, tomatoes and basil planted together can produce larger and more flavorful tomatoes.
- Attract pollinators: Companion plants can attract pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, which can help to improve pollination and fruit set.
How to Companion Plant
There are a few things to keep in mind when companion planting:
- Consider the needs of your plants: When choosing companion plants, it is important to consider the needs of your plants. For example, some plants need full sun, while others prefer partial shade.
- Plant compatible plants together: Not all plants are compatible with each other. Some plants can compete for water, nutrients, or space. It is important to do your research to make sure that you are planting compatible plants together.
- Plant companion plants in the right location: The location of your plants can also affect how well they grow together. For example, tall plants should be planted at the back of the garden, so that they do not shade shorter plants.
Conclusion
Companion planting is a great way to improve the health and productivity of your vegetable garden. By planting certain types of plants together, you can attract beneficial insects, repel pests, improve soil quality, and increase yields.
If you are new to companion planting, there are many resources available to help you get started. There are books, websites, and even smartphone apps that can provide you with information about companion planting combinations.
With a little planning, you can use companion planting to create a healthy and productive vegetable garden.
Companion planting is a gardening technique that involves planting certain plants together to benefit each other. Some companion plants can help to repel pests, attract beneficial insects, or improve the flavor of each other's fruits or vegetables.
If you're interested in learning more about companion planting, I recommend visiting the Gardenia Inspiration. This website has a comprehensive list of companion plants, as well as information on the benefits of companion planting.
In addition to the list of companion plants, the website also includes a section on how to plant companion plants together. This section includes tips on how to space plants, how to rotate crops, and how to create a companion planting plan.
I hope this information is helpful! If you have any other questions about companion planting, please feel free to leave a comment below.
FAQ of list of companion plants for vegetable gardens
Q: What are companion plants?
A: Companion plants are those that grow well together and can benefit each other in some way. They may attract beneficial insects, deter pests, improve soil quality, or provide shade.
Q: What are some good companion plants for vegetable gardens?
A: Here are some popular companion plants for vegetable gardens:
- Basil and tomatoes: Basil helps to repel thrips and other pests, and it also enhances the flavor of tomatoes.
- Marigolds: Marigolds repel nematodes, whiteflies, and other pests. They also attract pollinators, which help to improve fruit set.
- Nasturtiums: Nasturtiums attract aphids, which helps to keep them away from other plants. They also deter whiteflies and other pests.
- Beans and peas: Beans and peas fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits other plants. They also provide shade for some plants, such as carrots.
- Spinach and carrots: Spinach shades the soil around carrot plants, which helps to keep the soil cool and moist. Carrots also help to suppress weeds.
Q: What are some bad companion plants for vegetable gardens?
A: Here are some plants that should not be planted together:
- Tomatoes and potatoes: These plants are susceptible to the same diseases, so planting them together can increase the risk of infection.
- Carrots and celery: These plants compete for nutrients, so planting them together can stunt their growth.
- Cabbage and broccoli: These plants attract the same pests, so planting them together can make it more difficult to control pests.
Q: How do I know which companion plants are right for my garden?
A: There are a few things to consider when choosing companion plants for your garden:
- The type of plants you are growing: Some plants have specific needs, such as needing full sun or shade. Make sure to choose companion plants that have similar needs.
- The pests and diseases that are common in your area: Choose companion plants that will help to deter or control pests and diseases that are common in your area.
- Your personal preferences: Some people prefer to plant companion plants that have complementary flavors or colors.
Q: Where can I find more information about companion planting?
A: There are many resources available to learn more about companion planting. Here are a few suggestions:
- Books: There are many books available on companion planting. Some popular titles include "The Vegetable Gardener's Companion" by Louise Riotte and "Carrots Love Tomatoes" by Craig LeHoullier.
- Websites: There are many websites that offer information about companion planting. Some popular websites include www.gardeners.com and www.almanac.com.
- Local garden centers: Local garden centers often have staff who can offer advice on companion planting.
Image of list of companion plants for vegetable gardens
- Image 1: A colorful infographic showing which vegetables are good companion plants. The vegetables are grouped into different colors, with each color representing a different type of relationship between the plants. For example, red represents plants that attract beneficial insects, while green represents plants that repel pests.
- Image 2: A photo of a garden bed with a variety of companion plants. The plants are arranged in a way that takes their relationships into account. For example, tomatoes are planted near basil, which helps to repel pests.

- Image 3: A diagram showing how the roots of different plants interact with each other. Some plants have taproots, which grow deep into the soil, while others have shallow roots. Companion planting can help to improve the overall health of the soil by taking advantage of these different root systems.

- Image 4: A list of companion plants for specific vegetables. For example, beans are good companion plants for tomatoes, cucumbers, and corn.
- Image 5: A photo of a gardener harvesting vegetables from a companion-planted garden. The vegetables are healthy and abundant, thanks to the careful selection of companion plants.

Post a Comment for "The Ultimate Guide To Companion Planting For Vegetable Gardens"